

In particular, multiplying or adding two integers may result in a value that is unexpectedly small, and subtracting from a small integer may cause a wrap to a large positive value (for example, 8-bit integer addition 255 + 2 results in 1, which is 257 mod 2 8, and similarly subtraction 0 − 1 results in 255, a two's complement representation of −1). When an unsigned arithmetic operation produces a result larger than the maximum above for an N-bit integer, an overflow reduces the result to modulo N-th power of 2, retaining only the least significant bits of the result and effectively causing a wrap around.
set to the minimum or the maximum value in the representable range, rather than wrapped around. On some processors like graphics processing units (GPUs) and digital signal processors (DSPs) which support saturation arithmetic, overflowed results would be "clamped", i.e. The C11 standard states that for unsigned integers, modulo wrapping is the defined behavior and the term overflow never applies: "a computation involving unsigned operands can never overflow." In particular, if the possibility has not been anticipated, overflow can compromise a program's reliability and security.įor some applications, such as timers and clocks, wrapping on overflow can be desirable. modulo a power of the radix, usually two in modern computers, but sometimes ten or another radix).Īn overflow condition may give results leading to unintended behavior. The most common result of an overflow is that the least significant representable digits of the result are stored the result is said to wrap around the maximum (i.e. In computer programming, an integer overflow occurs when an arithmetic operation attempts to create a numeric value that is outside of the range that can be represented with a given number of digits – either higher than the maximum or lower than the minimum representable value. This is wrapping in contrast to saturating. All digits are set to the maximum 9 and the next increment of the white digit causes a cascade of carry-over additions setting all digits to 0, but there is no higher digit (1,000,000s digit) to change to a 1, so the counter resets to zero. We can use the sizeof() operator to check the size of a variable.Integer overflow can be demonstrated through an odometer overflowing, a mechanical version of the phenomenon.
#INTEGER FAQT TYPE 32 BIT#
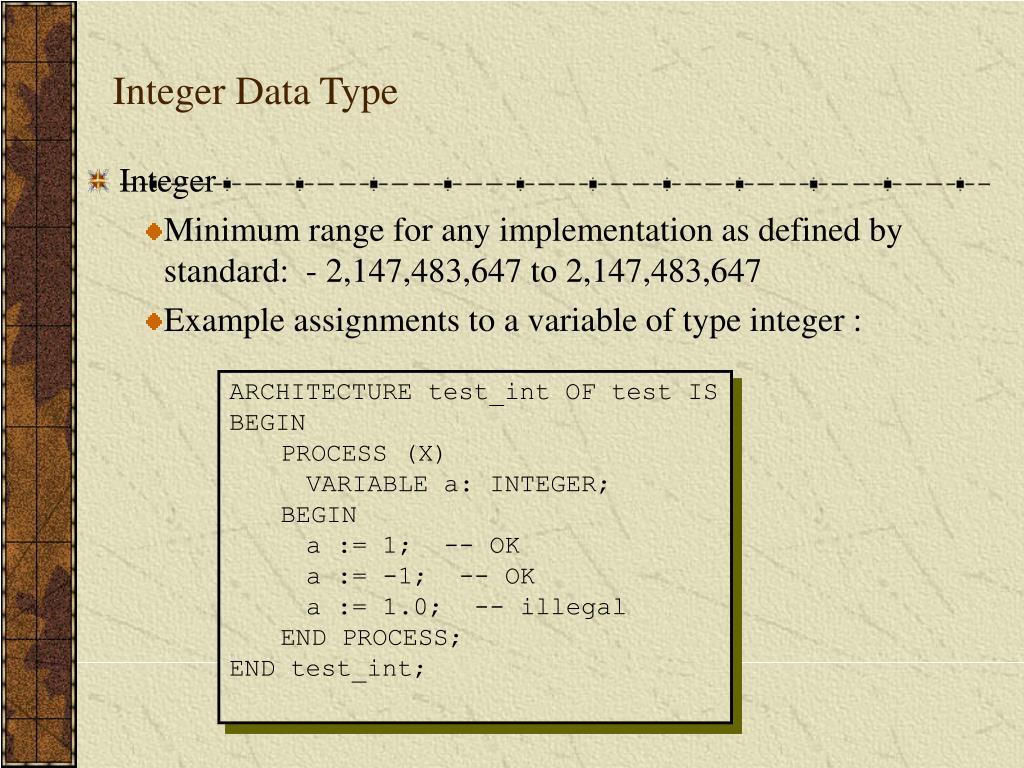
Below is list of ranges along with the memory requirement and format specifiers on 32 bit gcc compiler. These ranges may vary from compiler to compiler.

#INTEGER FAQT TYPE HOW TO#
How to pass a 2D array as a parameter in C?.How to dynamically allocate a 2D array in C?.Dynamic Memory Allocation in C using malloc(), calloc(), free() and realloc().Difference Between malloc() and calloc() with Examples.How to deallocate memory without using free() in C?.Initialization of static variables in C.Understanding “volatile” qualifier in C | Set 2 (Examples).What are the default values of static variables in C?.Difference between float and double in C/C++.Interesting facts about data-types and modifiers in C/C++.Is there any need of “long” data type in C and C++?.Comparison of a float with a value in C.ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
